
Our Office
2615 West 24th St.
Plainview, TX 79072
Existing Patients: (806) 296-6057
New Patients: (806) 217-7472
Visit Us Online
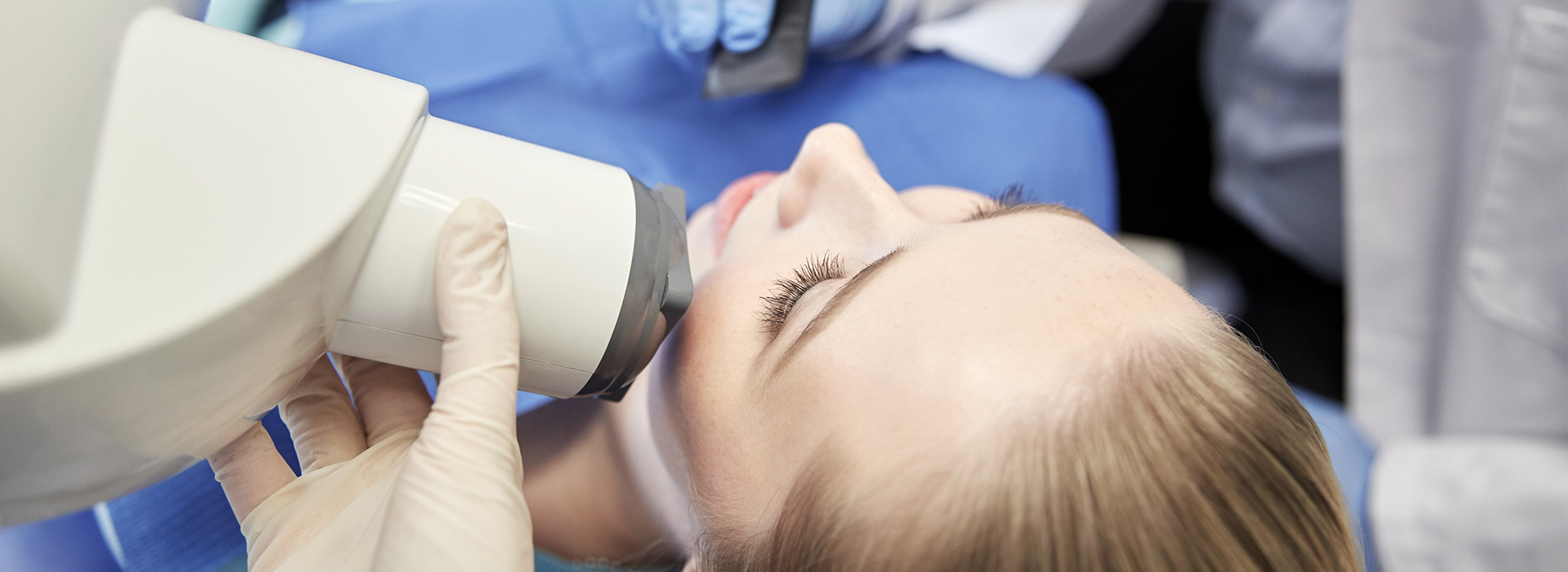
Digital radiography replaces traditional film with sensitive electronic sensors that capture X-ray images and send them directly to a computer. Instead of developing film with chemicals, the sensor converts X-ray energy into a digital file that can be viewed, adjusted, and stored instantly. For patients and clinicians alike, that shift from analog to digital means faster answers and clearer visuals, without the delays and handling associated with film processing.
The technology itself combines a compact sensor with specialized software that enhances, measures, and archives images. Clinicians can manipulate contrast, zoom in on areas of interest, and compare images side-by-side to spot subtle changes over time. This makes digital radiography a diagnostic tool that is both precise and adaptable to a wide range of dental concerns, from routine exams to more complex treatment planning.
Because the workflow is digital from capture to storage, images integrate seamlessly with modern electronic health records. That integration streamlines visits, reduces administrative steps, and helps ensure that every member of the dental team has immediate access to the same high-quality information—supporting coordinated, efficient care for patients of all ages.
One of the most noticeable differences patients experience is speed. With digital radiography, images appear on the screen within seconds of exposure, eliminating wait times for film development. This immediacy shortens chair time and allows the dentist to review findings with patients during the same appointment, which helps speed decision-making and reduces the number of visits required for diagnosis and planning.
The instant availability of images also benefits clinical workflow. If a retake is needed because of positioning, clinicians can correct it immediately rather than asking the patient to come back later. In busy practices, that flexibility keeps the schedule on track and reduces the likelihood of incomplete records or delayed treatments.
Beyond convenience, the ability to view images instantly supports clearer communication. Practitioners can show patients specific areas on-screen, annotate findings, and explain recommended next steps in real time. That transparency helps patients understand their oral health and feel more informed about proposed care.
Modern digital sensors are more sensitive to X-rays than traditional film, which means high-quality images can be captured with a smaller amount of radiation. The net effect is a meaningful reduction in a patient’s exposure during routine dental imaging—an important consideration for children, expectant parents, and patients who require periodic follow-up images.
Reducing dosage does not mean compromising diagnostic value. Digital systems often provide superior contrast and clearer depiction of fine details, especially when enhanced by software tools. Clinicians can adjust brightness and contrast or apply filters to highlight areas of concern, allowing confident diagnosis while keeping radiation levels as low as reasonably achievable.
For families and caregivers, that balance of safety and clarity offers peace of mind. Dentists who use digital radiography aim to follow professional guidelines for image frequency and technique, ensuring that every X-ray is justified by a diagnostic need and performed with patient safety as the priority.
Digital radiography enhances a clinician’s ability to detect problems early—before they become larger issues. High-resolution images reveal cavities between teeth, the extent of bone loss, the position of unerupted teeth, and the relationship of roots to surrounding structures. Early detection opens the door to more conservative treatments and better long-term outcomes.
Once an issue is identified, digital images become a central part of treatment planning. Dentists can measure structures precisely, evaluate progression over time with side-by-side comparisons, and plan restorative or orthodontic procedures with greater confidence. The software tools available with digital systems also help communicate complex findings to specialists when coordinated care is needed.
Because images are stored digitally, they are easy to retrieve for ongoing monitoring. Whether tracking the healing of a treated area or comparing annual checkups, long-term image records provide a reliable historical view that supports evidence-based decisions and continuity of care for growing children and adult patients alike.
At Texas Super Smiles for Kids, we prioritize gentle, family-centered care and use digital radiography as part of that commitment. Our team selects imaging methods and angles that minimize discomfort while still obtaining the diagnostic information needed. For children especially, we focus on positioning techniques and clear explanations to help reduce anxiety during X-ray procedures.
We also emphasize transparency with families: when X-rays are recommended, clinicians explain the reason for the image, what it will show, and how it will influence treatment recommendations. Visual aids from the digital image help parents and young patients see exactly what the dentist sees, making it easier to discuss options and next steps together.
Finally, our digital workflow supports coordination with other providers when additional care is needed. Images can be shared securely with specialists to ensure continuity and accuracy in referrals, all while keeping privacy and safety at the forefront of how we handle patient information.
Digital radiography is a modern, patient-focused approach to dental imaging that delivers clearer images, faster results, and lower radiation exposure. By combining sensitive electronic sensors with advanced software, clinicians can make more accurate diagnoses and craft treatment plans that protect long-term oral health—especially important for children and families.
If you’d like to learn more about how digital X-rays are used in our practice or what to expect at your child’s next visit, please contact us for more information. Our team is happy to answer your questions and explain how this technology helps us provide safe, effective care.
Digital radiography uses electronic sensors to capture X-ray images and convert X-ray energy into a digital file that appears immediately on a computer. Unlike traditional film, there is no chemical processing, which eliminates development delays and handling. This transition to digital improves workflow and gives clinicians faster access to diagnostic information.
Specialized imaging software enhances, measures, and archives images so clinicians can adjust contrast and zoom to examine fine detail. Images can be compared side-by-side to monitor changes over time, which aids in early detection and treatment planning. Because files integrate with electronic health records, the digital workflow supports coordinated care and efficient recordkeeping.
Yes, modern digital radiography is recognized as safe when used according to professional guidelines because sensors are more sensitive and require less radiation to produce diagnostic images. Dentists follow the ALARA principle—keeping exposure as low as reasonably achievable—when deciding which images are necessary. Protective measures such as fast sensors, precise positioning, and use of thyroid collars and lead aprons further reduce risk.
Frequency of X-rays for children is based on individual risk factors, age, and clinical need rather than a set schedule, so clinicians tailor imaging to minimize exposure. When X-rays are recommended, staff explain the purpose and how the image will help guide care, which helps parents feel informed. If parents have specific concerns about radiation, the dentist can review alternatives and imaging necessity during the visit.
Digital sensors are more efficient at capturing X-ray photons than traditional film, allowing clinicians to use lower doses while maintaining image quality. Software enhancements can compensate for lower exposure by improving contrast and detail without additional radiation. Modern equipment also supports techniques like rectangular collimation and pulsed X-ray emission that limit beam size and duration.
Proper technique and positioning reduce the need for retakes, which lowers cumulative exposure for the patient. Additionally, the immediate feedback of digital images allows staff to correct positioning on the spot rather than scheduling repeat appointments. Together, these factors make routine dental imaging safer while preserving diagnostic accuracy.
Digital X-rays reveal pathology and structural details that are not visible during a clinical exam, including interproximal cavities, bone loss from periodontal disease, and the position of unerupted or impacted teeth. They also show root anatomy, periapical changes, and restorations beneath the tooth surface that require further evaluation. High-resolution images and enhancement tools help clinicians identify early-stage problems before they become symptomatic.
Detecting these issues early often enables more conservative treatment and better long-term outcomes for patients. Stored images also allow precise measurements to guide procedures like root canals, extractions, and orthodontic planning. When complex care is needed, images can be reviewed with specialists to ensure coordinated, evidence-based decisions.
Digital images appear on the screen within seconds of exposure, which shortens chair time and allows the dentist to review findings with you during the same visit. If an image needs a retake because of positioning, the clinician can correct it immediately rather than asking you to return. This speed keeps appointments efficient and supports clearer communication about diagnosis and treatment options.
For children, staff use age-appropriate positioning techniques and simple explanations to make the process quick and comfortable. A small sensor is placed in the mouth for intraoral views and held steady for a few seconds while the image is captured. Team members aim to minimize discomfort and make the experience predictable so young patients remain calm.
Digital radiographs are archived within secure electronic health record systems, which allows clinicians to retrieve images quickly for comparison and long-term monitoring. These systems typically use encryption and access controls to protect patient information and comply with privacy regulations. Storing images digitally eliminates physical film handling and reduces the risk of misplacement or degradation over time.
When a specialist consultation or referral is needed, images can be shared electronically using secure transfer methods that preserve image quality and confidentiality. Clinicians control which images are shared and include relevant clinical notes to support coordinated care. Patients can ask the dental team how their images will be stored and who will have access if they have privacy concerns.
Digital radiographs provide the detailed visuals and measurement tools clinicians rely on for precise treatment planning across many procedures. For fillings, images help determine the extent of decay; for orthodontics, they show tooth position and root relationships; and for implants, they aid in assessing bone structure and proximity to vital anatomy. Enhanced images and comparison tools support informed decisions and help clinicians design treatment with greater confidence.
Stored images also allow the team to monitor healing and treatment progress over time, adjusting plans when necessary to achieve predictable results. When care involves multiple providers, sharing consistent digital images helps align goals and techniques between the general dentist and specialists. This collaborative approach supports continuity of care and helps ensure procedures are based on current, accurate information.
Yes, commonly used types include intraoral sensors for bitewing and periapical images, extraoral panoramic images for broad views of jaws and teeth, and three-dimensional cone-beam scans for complex cases. Intraoral images are ideal for detecting cavities and evaluating individual teeth, while panoramic images are useful for growth assessment, orthodontic planning, and screening large areas quickly. Cone-beam scans provide volumetric detail for implant planning, impacted teeth, and certain surgical evaluations when a 3-D view is necessary.
Clinicians select the smallest, most appropriate imaging modality that answers the clinical question while minimizing exposure, particularly for children. The choice depends on the diagnostic need, patient size and age, and the level of detail required for treatment planning. When advanced imaging is considered, dentists explain the reason and what information it will provide before proceeding.
At Texas Super Smiles for Kids, our team prioritizes gentle, family-centered care and uses proven positioning techniques to minimize discomfort during imaging. Staff employ age-appropriate explanations, distraction, and quick sensor placement to make the procedure less stressful for children. Protective shielding and careful handling further ensure safety and a calm experience for patients.
Clinicians take time to explain why each image is needed and how it will help guide care, which often eases anxiety for both children and parents. If a child needs extra reassurance, the team adapts their approach with slower positioning and coaching until the patient is comfortable. These small accommodations reduce movement and the need for retakes while building trust during visits.
If you have questions about radiation, imaging frequency, or what an X-ray shows, speak with your dentist or a member of the clinical team during your appointment. They can review specific images with you, explain findings in plain language, and describe how imaging informs treatment decisions. Open discussion helps parents understand the benefits and any alternatives before consenting to imaging.
For more detailed inquiries or to schedule a follow-up discussion, contact Texas Super Smiles for Kids during office hours and ask to speak with a clinician about radiographic care. Our team can clarify what to expect at your child's next visit and provide guidance tailored to your child's oral health needs. We welcome questions and strive to make imaging decisions transparent and family-focused.
